Actualidad
Nano-Encapsulated Biostimulants: Revolutionizing Growth and Postharvest Quality of Chili Fruits
Nano-encapsulated biostimulants significantly enhance chili plant growth, resilience, and postharvest quality by improving phytochemical content, photosynthetic efficiency, and controlled nutrient delivery
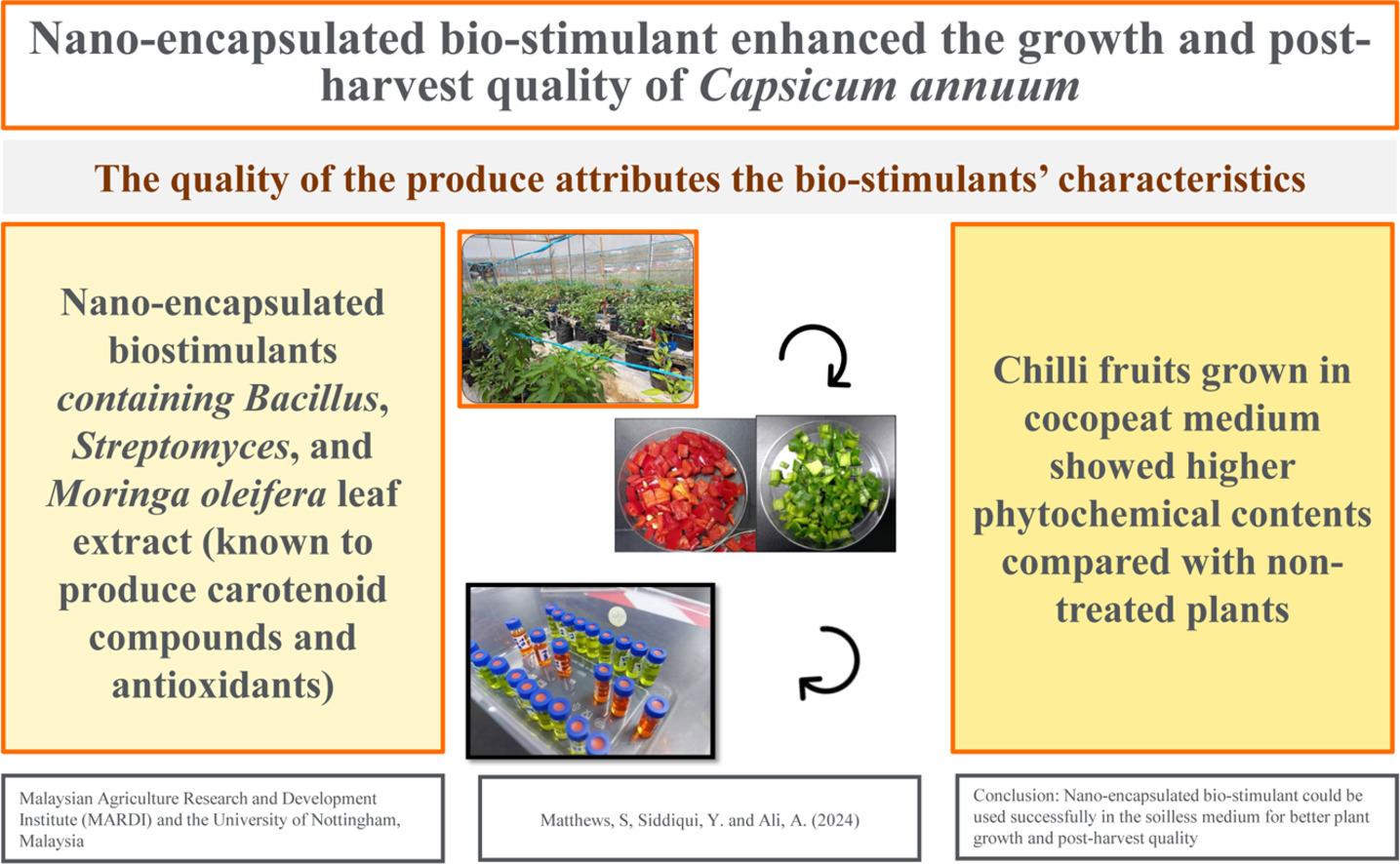
A groundbreaking study by Stella Matthews, Asgar Ali, and Yasmeen Siddiqui explores the impact of nano-encapsulated microbial and botanical biostimulants on the postharvest quality of chili peppers (Capsicum annuum). Published in Scientia Horticulturae (Volume 340, January 2025), the research highlights significant advancements in enhancing phytochemical content, improving plant growth, and ensuring better postharvest outcomes.
Key Highlights of the Study
Enhanced phytochemical content was observed, with red chilies treated with biostimulants showing higher flavonoid levels (15.77 ± 1.0 mg/L) compared to untreated ones (13.098 ± 1.8 mg/L). Treated chilies recorded elevated ascorbic acid levels, peaking at 144.29 ± 6.1 mg/L in red chilies. Capsaicin content was notably boosted during the early stages of chili development.
Biostimulant-treated chili plants achieved a mean height of 60 cm and a yield of 575.41 g, compared to 53 cm and 522.16 g in untreated plants. Quantum yield (photosynthetic capacity) was 0.618 in treated plants, outperforming the 0.581 of untreated plants.
Treated chili fruits exhibited superior color properties, with higher L-value and chroma values compared to untreated fruits.
Nano-encapsulation provided stability to the biostimulants, protecting active compounds from degradation and ensuring sustained efficacy.
Why Nano-Encapsulation Matters
Nano-encapsulation, a cutting-edge technology, enhances the stability and controlled release of bioactive compounds. This study demonstrates how encapsulated biostimulants protect against adverse environmental conditions, ensuring better absorption and consistent results. Benefits include prolonged microbial viability in formulations, improved delivery and efficiency of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), and enhanced resilience to storage and environmental challenges.
Implications for Agriculture
This research emphasizes the potential of nano-encapsulated biostimulants to transform the agricultural sector by mitigating climate change effects. By stimulating natural physiological processes, biostimulants help plants adapt to stress and climate variability. Nano-formulations reduce degradation, minimizing application frequency and overall costs. The ability to boost phytochemical content offers superior produce quality, aligning with consumer preferences for nutrient-rich foods.
Conclusion
This pioneering study provides a robust framework for the development of advanced biostimulant formulations. Nano-encapsulation emerges as a vital tool for enhancing the growth, resilience, and postharvest quality of chili fruits, with promising applications across other crops.
Source
Nano-encapsulated biostimulant enhances growth and postharvest quality of chili peppers (Capsicum annuum)
Stella Matthews, Asgar Ali, Yasmeen Siddiqui
Scientia Horticulturae Volume 340, 15 January 2025, 113920
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304423824010720
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2024.113920










