Actualidad
Nano-nutrient formulations, positive effects on postharvest behaviour
Nanoscale nutrients improve the nutritional value of fruits and vegetables and the shelf lives
A novel approach to improving the growth and quality of fruits and vegetables while prolonging their shelf life is the use of nano-nutrient formulations in agriculture.
Examining the state of the art in nanonutrient formulation research, this review highlights the effects of these formulations on crop productivity and postharvest preservation.
Nano-zinc, nano-iron, and nano-calcium
The development of nano-sized nutrient formulations, namely nano-zinc, nano-iron, and nano-calcium, has resulted from the application of nanotechnology in agriculture.
These combinations increase the uptake and utilization of nutrients by plants by improving their delivery. The precise and continuous supply of nutrients is ensured by the regulated release mechanism of nano-sized particles, which promotes healthy growth and produces fruits and vegetables with higher nutritional value and longer shelf lives.
Analyzed research demonstrates how important growth metrics are positively impacted by nanonutrient formulations.
Furthermore, these nutrients in nanoscale form improve disease resistance and stress tolerance and improve crop yield and reduced post-harvest losses.
About fertilizers and pesticides in nano-sizes
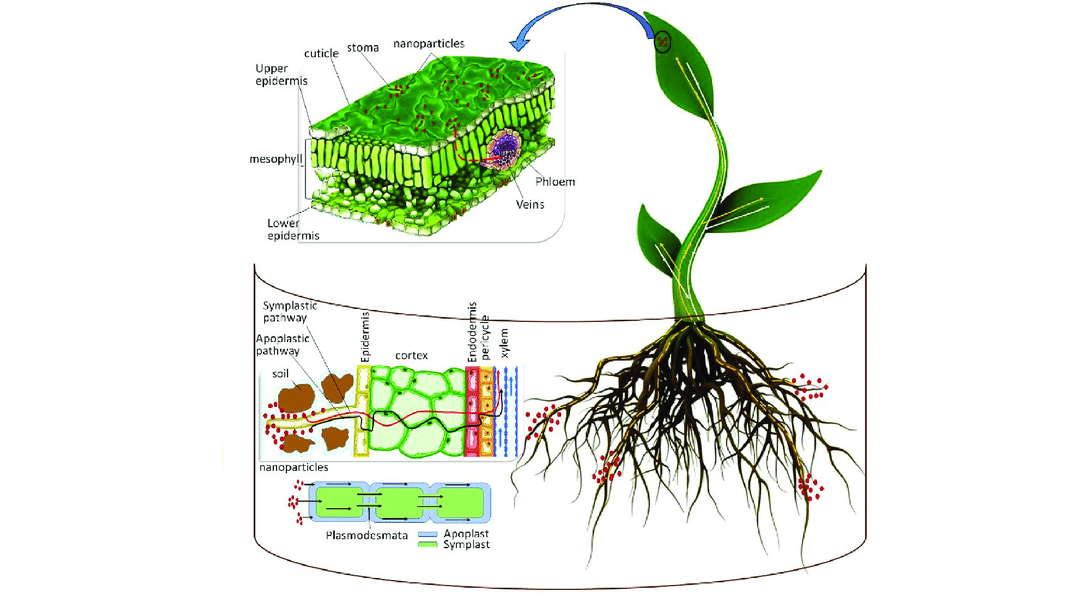
The review by Mohamed T. El-Saadony et al., (2021) presents an overview about the biosynthesis of nanoparticles, NPs, using NPs as nano-fertilizers and nano-pesticides, the applications of NPs in agriculture, and their role in enhancing the function of biofactors.
The paper also shows recent studies on NPs-plant interactions, the fate and safety of nanomaterials in plants, and NPs' function in alleviating the adverse effects of abiotic stress and heavy metal toxicity.
Nano-fertilizers are essential to reduce the use of inorganic fertilizers and reduce their antagonistic effects on the environment. Nano-fertilizers are more reactive, can penetrate the epidermis allowing for gradual release, and targeted distribution, and thus reducing nutrients surplus, enhancing nutrient use efficiency.
NPs are crucial in alleviating abiotic stress and heavy metal toxicity. However, some studies reported the toxic effects of NPs on higher plants by induction of oxidative stress signals via depositing NPs on the cell surface and in organelles.
This review article defines limitations and perspectives of using nano-fertilizers as an alternative to conventional fertilizers.
Sources
Sravani, V., Rajeswari, R., Gopalakrishnan, M., Senthil Kumar, M., Kavitha, M., & Bharathi, C. (2024)
Nanonutrient Formulations – Impact on Growth and Post-Harvest Quality of Fruits and Vegetables
Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2024.2431633
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00103624.2024.2431633
Vital roles of sustainable nano-fertilizers in improving plant quality and quantity-an updated revie (2021)
Mohamed T. El-Saadony, Ameina S. ALmoshadak, Manal E. Shafi, Najah M. Albaqami, Ahmed M. Saad, Amira M. El-Tahan, El-Sayed M. Desoky, Ahmed S.M. Elnahal, Aisha Almakas, Taia A. Abd El-Mageed, Ayman E. Taha j, Ahmed S. Elrys & Ayman M. Helmy
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, Volume 28, Issue 12, December 2021, Pages 7349-7359
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.08.032
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319562X2100718X
The picture is Fig 2 - Mechanism of action by nano-fertilizer, of the paper by Mohamed T. El-Saadony et al.











